
What Are the Symptoms of Hand Foot Mouth Disease?
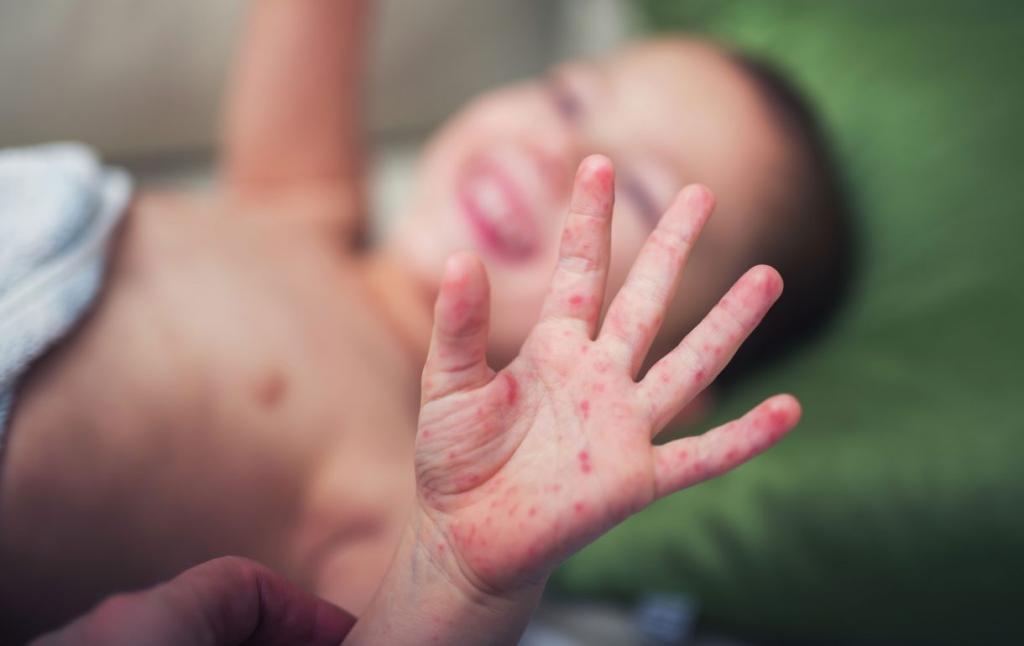
Hand, foot and mouth disease usually begins with fever, anorexia, malaise and sore throat. Abdominal pain and cough. 1-2 days after the onset of the fever, painful, water-filled rashes occur in the mouth, called herpanjina. The rashes usually begin as small red spots on the back of the mouth, then become bubbles filled with water and often explode and explodes. Skin rash develops after 1-2 days. The rashes that begin as flat red dots in the palm of the foot base and hands, then collects water. Sometimes rashes can occur in the knees, elbows, buttocks, or in the genital area. Spills in the hands and feet usually heal spontaneously within 5-7 days.
Especially young children may have difficulty in drinking water due to painful wounds in their mouths and dehydration may occur.
Although the name is Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease, there may not always be rash in all these areas. It may only develop in the form of mouth sores or skin rashes only.
How is the disease transmitted?
The mean incubation period is 3-6 days. Viruses that cause hand, foot and mouth disease can be found in the infected person's nose and throat secretions, fluid in the rash, and stool (stool). Close personal contact with infected persons can be transmitted by contact with feces, by contact with feces, by air, by coughing or sneezing. It is rarely possible to swallow water in swimming pools or water parks, but to take the active virus. The contamination of infected people is higher in contaminated waters, and a good chlorination may be insufficient.
Generally, a person with hand, foot and mouth disease is very high in the first week of the disease. Even after the symptoms have disappeared, they can sometimes be infectious for days or weeks. In particular, virus-infected adults may be infectious, although they do not show any symptoms. Since the infectivity is very high, it is useful to isolate the patient until the symptoms are completely eliminated.
Hand-foot-mouth disease is a common viral disease that usually affects infants and children under 5 years of age, but is sometimes seen in adults. The most common cause is Coxsackie virus A16. Enterovirus 71 can lead to outbreaks of hand-foot mouth disease. It is often seen in summer or in the first months of autumn.
How to Diagnose?
A detailed history of the disease and physical examination, characteristic rashes in the mouth, hands and feet are usually sufficient for the diagnosis of the disease. Differential diagnosis should be made with diseases such as aphthous stomatitis, chicken pox, erythema multiforme and herpes simplex.
Generally, no laboratory work is required. The number of leukocytes is between 4000-16,000 / ml. Sometimes atypical lymphocytes are present.
What are the prevention measures of disease?
There is no vaccine developed to prevent disease. It is necessary to avoid contact with sick individuals and to protect against illness by paying attention to some basic cleaning rules.
Your hands should be washed with plenty of water and soap, especially after toilet use or after changing diapers, before preparing or eating.
You must correct surface disinfecting and disinfection of all materials, including toys.
You should avoid close contact with the patient (such as kissing, hugging, etc.) and the use of common cups.
There is no special treatment of the disease.
Some measures may be taken to relieve symptoms; Fever and painkillers can be used for pain and fever. For painful mouth sores, mouthwashes, mouth water or sprays may be used.